#What’s a suborbital flight? An aerospace engineer explains

Table of Contents
“#What’s a suborbital flight? An aerospace engineer explains”
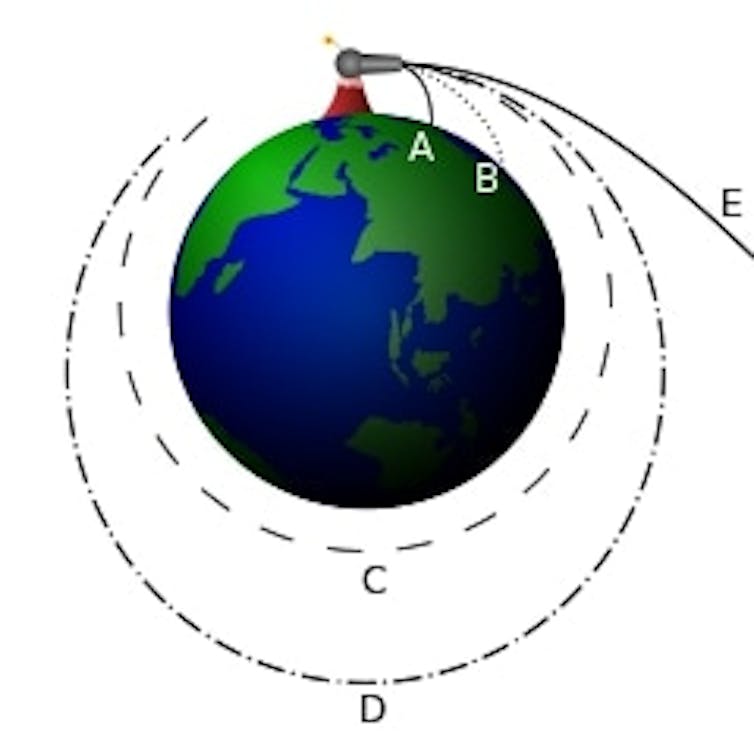
But what exactly is “suborbital”? Simply put, it means that while these vehicles will cross the ill-defined boundary of space, they will not be going fast enough to stay in space once they get there.
If a spacecraft – or anything else, for that matter – reaches a speed of 17,500 mph (28,000 km/h) or more, instead of falling back to the ground, it will continuously fall around the Earth. That continuous falling is what it means to be in orbit and is how satellites and the Moon stay above Earth.
Anything that launches to space but does not have sufficient horizontal velocity to stay in space – like these rockets – comes back to Earth and therefore flies a suborbital trajectory.
Why these suborbital flights matter
Although the two spacecraft launched in July 2021 will not reach orbit, the accomplishment of reaching space in private spacecraft is a major milestone in the history of humanity. Those aboard these and all future private-sector, suborbital flights will for a few minutes be in space, experience a few minutes of exhilarating weightlessness, and absolutely earn their astronaut wings.
A well-thrown baseball
Conceptually, the flights that Branson and Bezos will be on are not terribly different from a baseball thrown into the air.
The faster you can throw the baseball upward, the higher it will go and the longer it will stay in the air. If you throw the ball with a bit of sideways velocity as well, it will go farther down-range.
Imagine throwing your baseball in an open field. As the ball rises, it slows down, as the kinetic energy inherent in its velocity is exchanged for potential energy in the form of increased altitude. Eventually, the ball will reach its maximum height and then fall back to the ground.
Now imagine that you could throw the baseball fast enough to reach a height of perhaps 60 miles (97 km). Presto! The baseball has reached space. But when the ball reaches its maximum height, it will have zero vertical velocity and start to fall back to Earth.
The flight may take several minutes, and during most of that time, the ball would experience near weightlessness – as will the newly minted astronauts aboard these spacecraft. Just like the hypothetical baseball, the astronauts will reach space but won’t enter orbit, so their flights will be suborbital.
This article by John M. Horack, Neil Armstrong Chair and Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, The Ohio State University is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more like this article, you can visit our Technology category.




