#Signals from muscle protect from dementia

“#Signals from muscle protect from dementia”
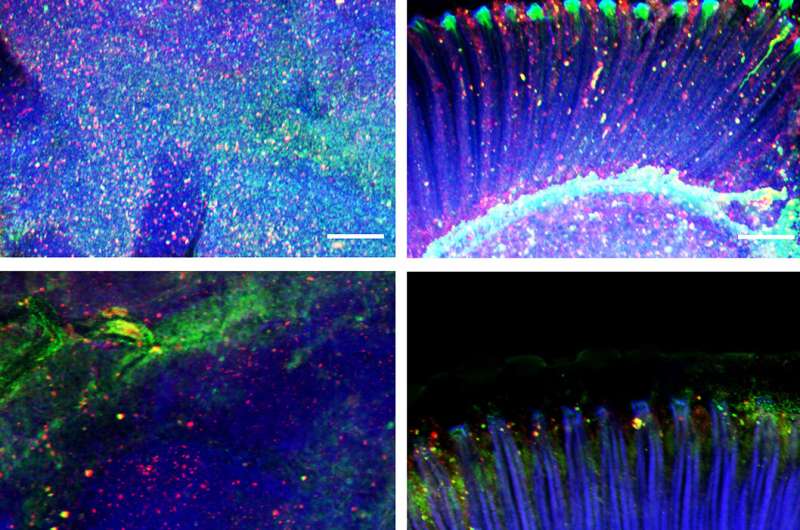
How do different parts of the body communicate? Scientists at St. Jude are studying how signals sent from skeletal muscle affect the brain.
The team studied fruit flies and cutting-edge brain cell models called organoids. They focused on the signals muscles send when stressed. The researchers found that stress signals rely on an enzyme called Amyrel amylase and its product, the disaccharide maltose.
The scientists showed that mimicking the stress signals can protect the brain and retina from aging. The signals work by preventing the buildup of misfolded protein aggregates. Findings suggest that tailoring this signaling may potentially help combat neurodegenerative conditions like age-related dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
“We found that a stress response induced in muscle could impact not only the muscle but also promote protein quality control in distant tissues like the brain and retina,” said Fabio Demontis, Ph.D., of St. Jude Developmental Neurobiology. “This stress response was actually protecting those tissues during aging.”
Cell Metabolism published a report on this work.
Research reveals how muscles talk to the brain to regulate feeding behavior
Mamta Rai et al, Proteasome stress in skeletal muscle mounts a long-range protective response that delays retinal and brain aging, Cell Metabolism (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.005
Citation:
Signals from muscle protect from dementia (2021, March 26)
retrieved 26 March 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-03-muscle-dementia.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.