#Researchers report smallest finFET-based biosensor for high-sensitivity molecule detection

“#Researchers report smallest finFET-based biosensor for high-sensitivity molecule detection”
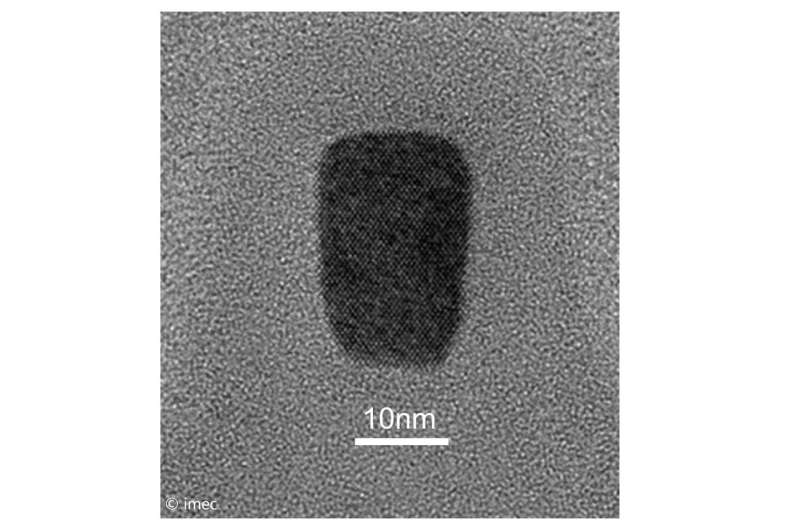
Imec has presented the smallest silicon finFET that functions as a biosensor. Achieving ultrasmall dimensions (13 nm fin width and 50 nm gate length) and fabricated with a CMOS-compatible process flow in imec’s 300 mm cleanroom, imec envisions volume manufacturing and integration into high-throughput, cost-effective detection tools, with tens of thousands of these BioFETs working in parallel. With a demonstrated detection limit of tens of molecules today, imec ultimately targets highly accurate BioFETs sensing single DNA molecules.
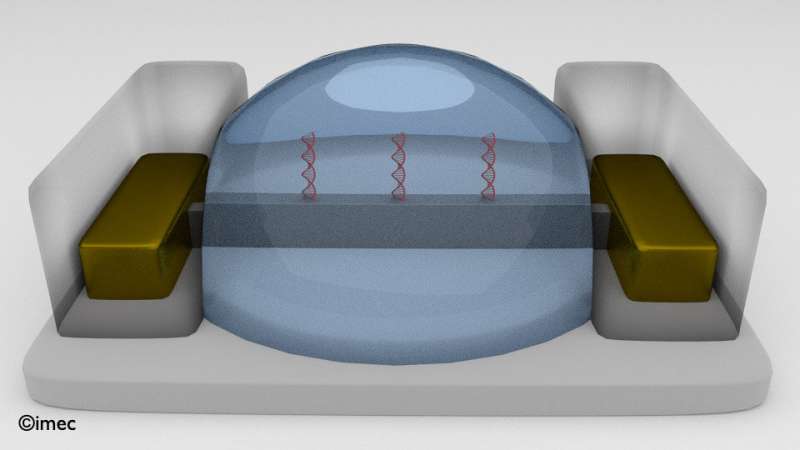
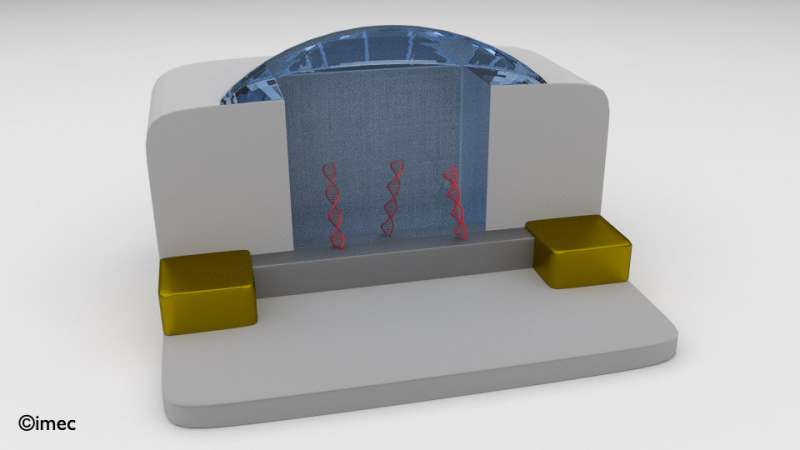
Due to its high integration and low cost potential, field-effect transistors (FETs) have gained a lot of interest for biosensing applications such as DNA, protein and virus detection and pH sensing. When biomolecules bind to the chemically modified dielectric surface of the gate, its threshold voltage changes, resulting in a measurable signal. Despite continuous research progress in this field, BioFET devices have not yet delivered all their potential into successful products. Imec has explored how an advanced generation of CMOS FET devices, so called finFETs with three-dimensional short length gates can improve the sensitivity of BioFETs and open new applications. These finFETS have advantages in view of high integration and parallelization but very little was understood about their potential as a BioFET.
With its bio finFET devices with lengths down to 50 nanometers, imec has demonstrated a robust signal for DNA hybridization and the detection of tens of DNA molecules on the surface of nano-scale finFETs. Based on experiments and simulation, imec predicts single-molecule detection with a signal to noise ratio (SNR) > 5 to be possible with sub-70 nm finFETs.
“By virtue of our insatiable hunger for ever faster computation and data access, the semiconductor industry has gotten to a point where we can now integrate a very large number of nanoscale devices into incredibly complex systems and this on just a few square millimeters of silicon using mass manufacturing approaches that achieve nearly atomic precision,” said Peter Peumans, CTO Health technologies at imec. “We are leveraging these capabilities not only to build better computers or communication devices, but to enable chip-based tools for the life sciences that are game-changing in their ability to reveal details about biology that were hitherto inaccessible.”
More information:
IEDM 2021 paper 35.4 50 nm Gate Length FinFET Biosensor & the Outlook for Single-Molecule Detection
Citation:
Researchers report smallest finFET-based biosensor for high-sensitivity molecule detection (2021, January 18)
retrieved 18 January 2021
from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-01-smallest-finfet-based-biosensor-high-sensitivity-molecule.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.


