#Psychosocial support interventions in medical settings can improve survival

“#Psychosocial support interventions in medical settings can improve survival”
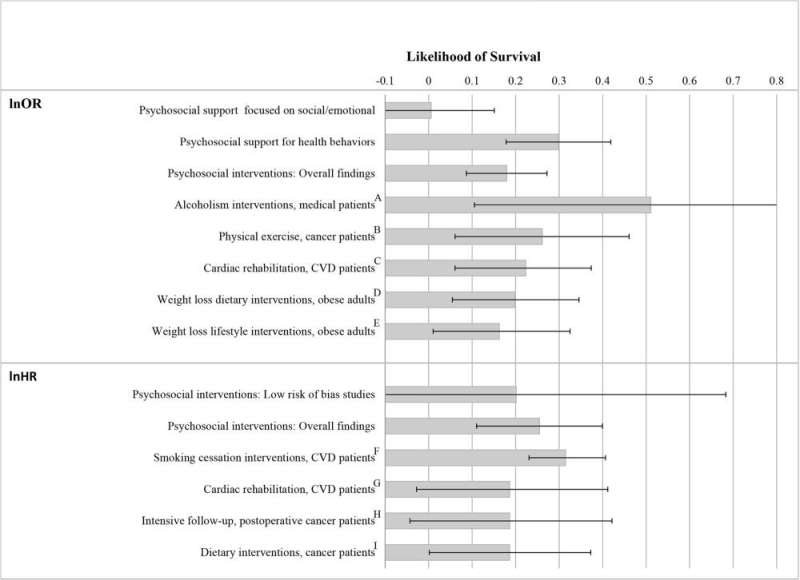
Psychosocial support interventions that promote the health behaviors of patients in medical settings improve survival, according to a study published May 18 in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Timothy B. Smith of Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, United States and colleagues. On average, psychosocial interventions prolonged medical patient life to the same extent as cardiac rehabilitation or treatments for alcoholism or smoking.
Hospitals, clinics, and health organizations have provided psychosocial support interventions for patients to supplement medical care. But variability exists among psychosocial interventions, and prior reviews of interventions augmenting psychosocial support in medical settings have reported mixed outcomes. Smith and his collaborators conducted a meta-analysis to assess the effectiveness of psychosocial support interventions in improving patient survival, and to identify factors associated with greater effectiveness. The authors searched the literature for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that were published from 1980 to 2020, and focused their analysis on 106 RCTs including a total of 40,280 patients in inpatient and outpatient health care settings.
Among 87 RCTs reporting data for discrete time periods, there was a 20% increased likelihood of survival among patients receiving psychosocial support compared to control groups receiving standard medical care. Among those studies, psychosocial interventions explicitly promoting health behaviors improved the likelihood of survival, whereas interventions without that primary focus did not. Across 22 RCTs reporting survival time, psychosocial interventions were associated with a 29% increased probability of survival over time. Studies with patients having relatively greater disease severity tended to yield smaller gains in survival time relative to control groups. According to the authors, future psychosocial support interventions targeted at medical patients should address health behaviors such as motivation to adhere to treatments rather than focusing solely on emotional and psychological support.
Psychotherapy may help multiple sclerosis patients
Smith TB, Workman C, Andrews C, Barton B, Cook M, Layton R, et al. (2021) Effects of psychosocial support interventions on survival in inpatient and outpatient healthcare settings: A meta-analysis of 106 randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med 18(5): e1003595. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003595
Citation:
Psychosocial support interventions in medical settings can improve survival (2021, May 18)
retrieved 18 May 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-05-psychosocial-interventions-medical-survival.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.



