#Yashahime: Princess Half-Demon – Crunchyroll Fall 2020 Spotlight

“#Yashahime: Princess Half-Demon – Crunchyroll Fall 2020 Spotlight”

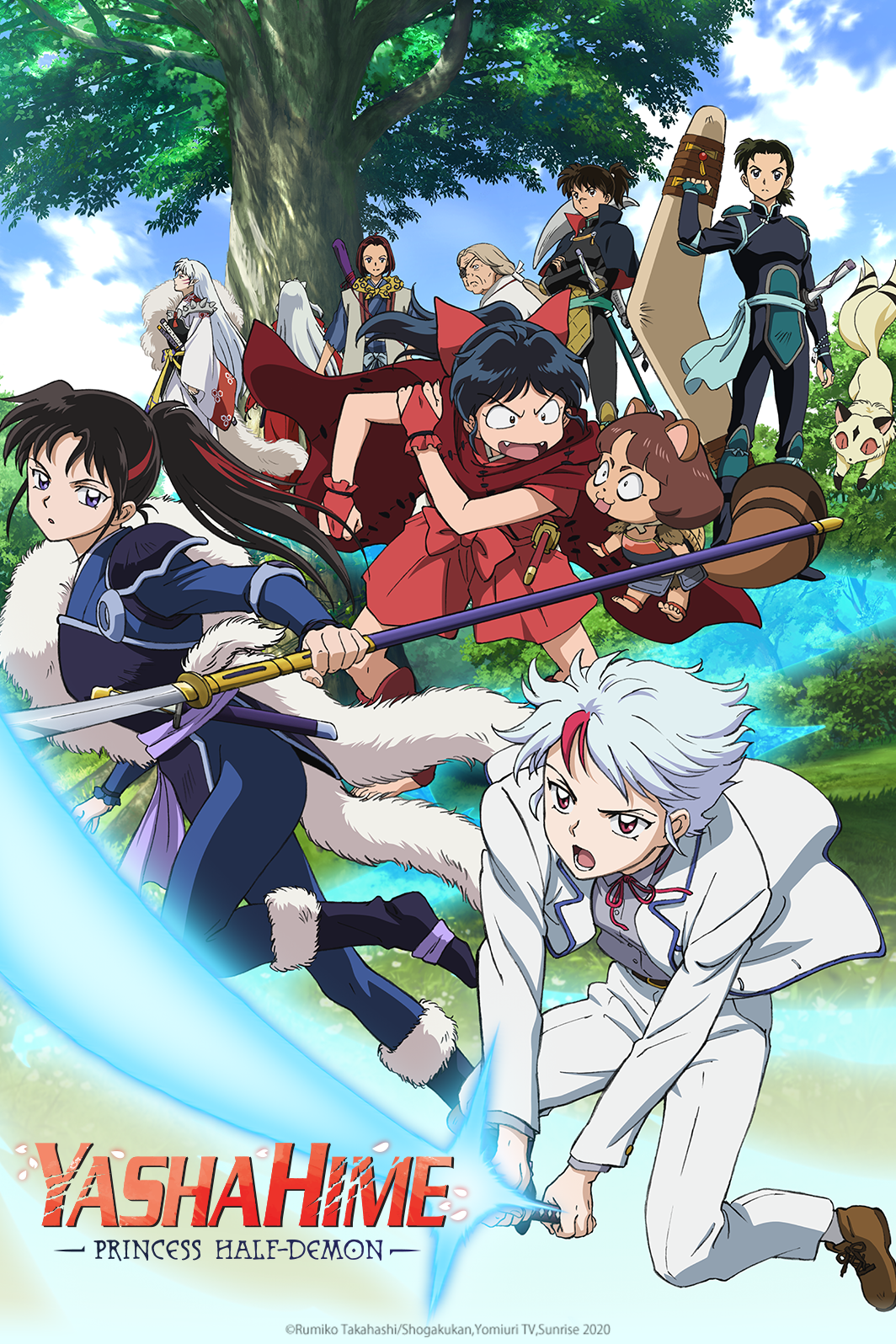
Inuyasha fans were met with a surprise treat when word first got out about Yashahime: Princess Half-Demon, which follows up on Rumiko Takahashi's classic series with a story centered on the daughters of Sesshomaru and Inuyasha. Now Yashahime is nearly upon us as part of the Crunchyroll Fall 2020 Spotlight, and you can get all the details ahead of the premiere below.

Navigation
Launch Time: October 3 at 3:00am PT
Territories: US, Canada, LatAM, EMEA
Show Page (Coming Soon!)
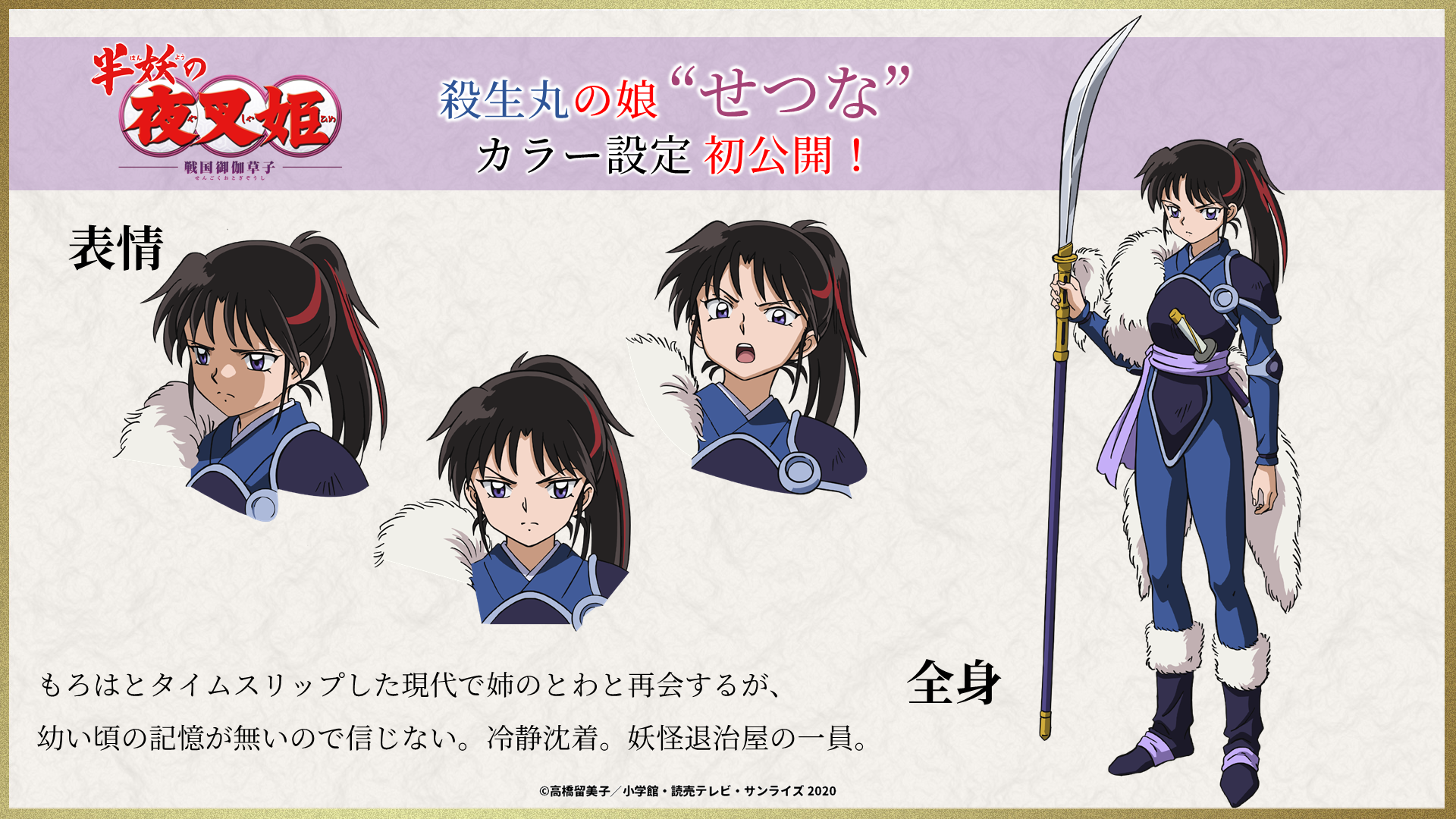
Yashahime: Princess Half-Demon follows the daughters of Sesshomaru and Inuyasha as they set out on a journey transcending time. Set in feudal Japan, half-demon twins Towa and Setsuna are separated from each other during a forest fire. While desperately searching for her younger sister, Towa wanders into a mysterious tunnel that sends her into present-day Japan, where she is found and raised by Kagome Higurashi’s brother, Sota, and his family. Ten years later, the tunnel that connects the two eras has reopened, allowing Towa to be reunited with Setsuna, who is now a demon slayer working for Kohaku. But to Towa’s shock, Setsuna appears to have lost all memories of her older sister. Joined by Moroha, the daughter of Inuyasha and Kagome, the three young women travel between the two eras on an adventure to regain their missing past.
Towa Higurashi
VA: Sara Matsumoto (Namida Suzuno in BORUTO: NARUTO NEXT GENERATIONS)

Setsuna
VA: Mikako Komatsu (Madoka Kaguya / Cure Selene in Star☆Twinkle PreCure)
Moroha
Azusa Tadokoro (Aoi Kiriya in Aikatsu!)

Director
Teruo Sato (Inuyasha episode director)
Screenplay
Katsuyuki Sumisawa (Inuyasha)
Animation Character Designs
Yoshihito Hishinuma (Inuyasha)
Main Character Designs
Rumiko Takahashi
Art Director
Shigemi Ikeda
Yukiko Maruyama
Music
Kaoru Wada (Inuyasha)
Opening Theme Performer
SixTONES
Ending Theme Performer
Uru
Animation Production
SUNRISE
Shortly after the series was first announced, Inuyasha creator Rumiko Takahashi shared her character designs for the main cast. Here's Takahashi's original take on:
Towa Higurashi:

Setsuna:

Moroha:

And a height comparison between all three:

——-
Joseph Luster is the Games and Web editor at Otaku USA Magazine. You can read his webcomic, BIG DUMB FIGHTING IDIOTS at subhumanzoids. Follow him on Twitter @Moldilox.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more anime-manga articles, you can visit our anime-manga category.