#Study highlights lack of evidence for plasticity-led evolution in lizards

“#Study highlights lack of evidence for plasticity-led evolution in lizards”
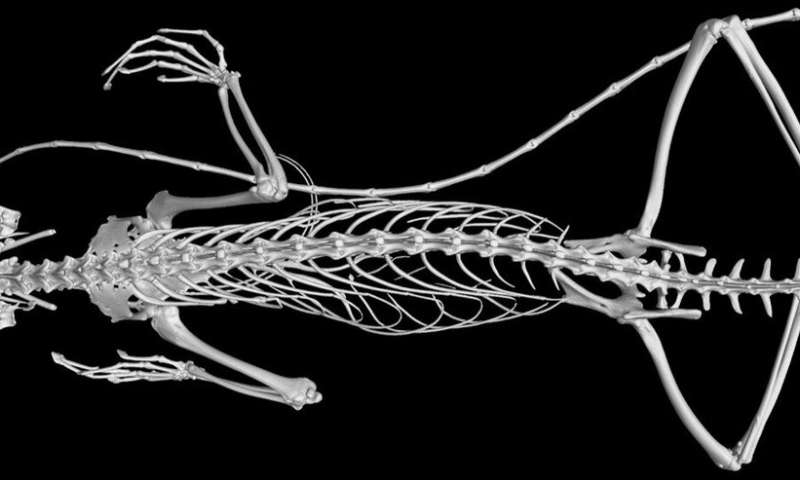
Scientists have challenged a popular theory behind the evolution of similar traits in island lizards, in a study published recently in eLife.
The findings in Greater Antillean Anolis lizards provide insights on why creatures often evolve similar physical features independently when living in similar habitats. They suggest that the role of developmental plasticity in shaping adaptive evolution may be less important than commonly thought.
Developmental plasticity refers to how development responds to the environment, in particular the way that an organism’s genetic constitution (or genotype) interacts with its environment during development to produce a particular set of characteristics (or phenotype).
“Anolis lizards that live on all four of the Greater Antillean islands have independently and repeatedly evolved six different body types for maneuvering through their given habitat,” says lead author Nathalie Feiner, Researcher at the Department of Biology, Lund University, Sweden. “As a result, they make a great model for studying why evolution often repeats itself.”
To address this question, Feiner and the team used micro computed tomography scans to measure the shoulder, hip and leg bones of 95 species of anoles that live on the Greater Antillean islands. Their work revealed that several of the species’ body shapes evolved along similar trajectories.
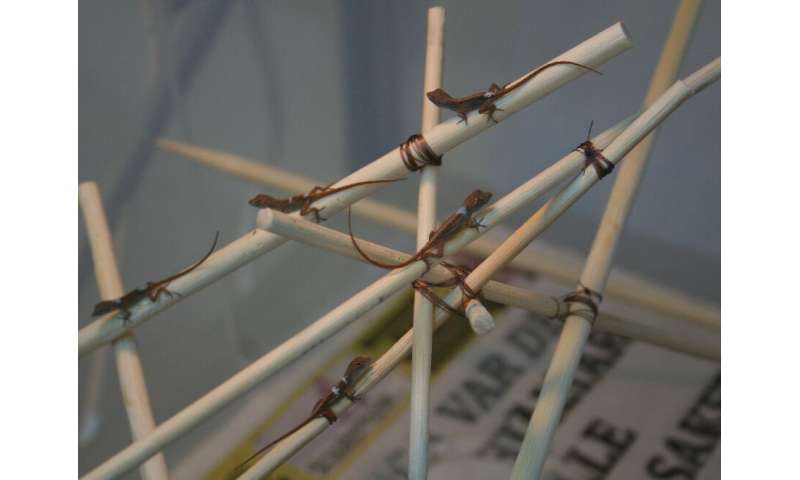

“These body shapes are adapted by natural selection, but several different shapes could in principle perform equally well in a given habitat,” says senior author Tobias Uller, Professor of Evolutionary Biology at the Department of Biology, Lund University. “As a result, repeated evolution is more likely to occur when species share a developmental biology that makes some characteristics appear readily, while others are rare or even impossible.”
One source of these developmental biases can be found in how individuals respond to different environments, a hypothesis known as plasticity-led evolution. The researchers tested how the anoles’ bones responded to stresses induced by climbing and running to see if these changes directly matched the skeletal structure (or morphology) of those specialized to a given habitat.
To do this, they raised two groups of anoles—some that typically perch on narrow twigs, and others that typically run and climb on tree trunks—on two different types of surfaces, which changed the way the animals moved or perched, as well as their morphology. However, these changes were poorly matched to the evolutionary divergence between habitat specialists that evolved repeatedly on different islands.
“The responsiveness of bone to mechanical stress is a good candidate for plasticity-led evolution,” Feiner explains. “But this responsiveness does not seem to have channeled the evolution of the locomotor skeleton in Anolis lizards. Instead, our findings suggest that the morphologies that evolved again and again in these lizards are likely due to simple genetic changes.”
New study sheds light (and some shade) on anole diversification
Nathalie Feiner et al, Plasticity and evolutionary convergence in the locomotor skeleton of Greater Antillean Anolis lizards, eLife (2020). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57468
Citation:
Study highlights lack of evidence for plasticity-led evolution in lizards (2020, September 29)
retrieved 29 September 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-09-highlights-lack-evidence-plasticity-led-evolution.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.



