#Achieving cost-efficient superalloy powder manufacturing using machine learning

“#Achieving cost-efficient superalloy powder manufacturing using machine learning”
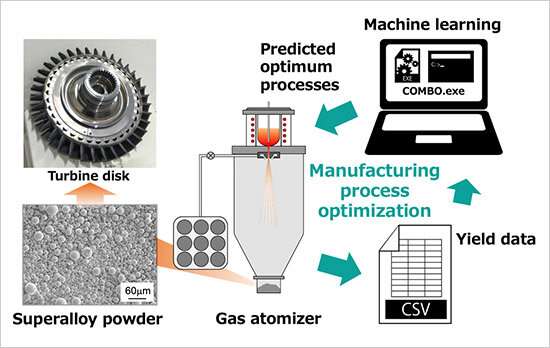
High-performance, high-quality Ni-Co-based superalloy powders are promising aircraft engine raw materials. Using machine learning, a NIMS team has succeeded in speedily determining the optimum parameters for manufacturing these types of powders at high yields. The team then demonstrated that these parameters actually led to the low-cost manufacturing of powders suitable for high-pressure turbine disk production. The use of this technique may significantly reduce the cost of practical, large-scale manufacturing of superalloy powders.
Metal 3-D printing has been rapidly adopted in aerospace engine production, leading to growing demand for low-cost manufacturing and supply of the alloy powders these printing techniques require. When these materials are used in the production of high-pressure turbine disks—a core engine component—they need to meet particularly rigorous requirements: they have to be heat-resistant, highly plastic, high-quality and homogeneous superalloy powders that can be processed into spheres. They also need to be produced at high yields to reduce costs. In practical manufacturing settings, superalloy powders are commonly produced for this purpose using large gas atomizers. It is therefore important to optimize a number of manufacturing parameters, such as the temperatures used to melt metals and the gas pressures. However, this optimization process has proven to be enormously costly, time-consuming and labor-intensive even with the assistance of knowledgeable and experienced experts.
This research team used machine learning in an attempt to optimize gas atomization processes for the manufacturing of Ni-Co-based superalloy powders suitable for high-pressure turbine disk production without relying on the knowledge of experts. As a result, the team succeeded in manufacturing fine-grained powders that can be processed into spheres. In addition, use of the parameters dramatically increased production yields from the conventional 10 to 30% to approximately 78% after performing experiments only six times without using previously collected data. The powder manufactured in this research was approximately 72% cheaper than commercially available powders when the prices of the raw materials were compared.
After years of R&D, NIMS has developed techniques for designing superalloys with controlled physical properties, such as heat resistance. The combined use of these techniques and the parameter optimization technique developed in this research is expected to enable low-cost production of functional superalloy powders designed to meet specific purposes. The prediction accuracy of machine learning models increases as they receive more training data. Superalloy powder manufacturers in the private sector possess largely unexploited manufacturing process data. Integrating this data may further improve the ability of our technique to predict optimum parameters, potentially enabling the manufacturing of higher-quality powders at lower cost.
This research was published in Materials & Design, an open-access journal.
Ryo Tamura et al. Machine learning-driven optimization in powder manufacturing of Ni-Co based superalloy, Materials & Design (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109290
Citation:
Achieving cost-efficient superalloy powder manufacturing using machine learning (2021, January 25)
retrieved 26 January 2021
from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-01-cost-efficient-superalloy-powder-machine.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.



