#Scientists detect water vapour emanating from Mars

“#Scientists detect water vapour emanating from Mars”
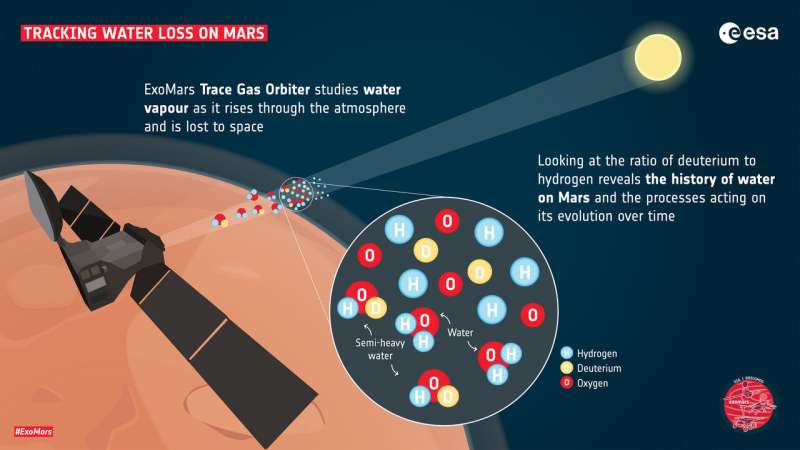
Researchers said Wednesday they had observed water vapour escaping high up in the thin atmosphere of Mars, offering tantalising new clues as to whether the Red Planet could have once hosted life.
The traces of ancient valleys and river channels suggest liquid water once flowed across the surface of Mars. Today, the water is mostly locked up in the planet’s ice caps or buried underground.
But some of it is vaporising, in the form of hydrogen leaking from the atmosphere, according to the new research co-authored in the journal Science Advances by two scientists at Britain’s Open University.
They detected the vapour by analysing light passing through the Martian atmosphere using an instrument called the Nadir and Occultation for Mars Discovery.
The device is travelling aboard the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, a joint mission between the European Space Agency and Russia’s Roscosmos.
“This fantastic instrument is giving us a never-before-seen view of water isotopes in the atmosphere of Mars as a function of both time and location,” Manish Patel, senior lecturer in planetary sciences at the Open University, said.
“Measuring water isotopes is a crucial element of understanding how Mars as a planet has lost its water over time, and therefore how the habitability of the planet has changed throughout its history,” he said.
It has been a busy week for Martian research.
On Wednesday, the Chinese Tianwen-1 probe entered the planet’s orbit after launching from southern China last July, in the latest advance for Beijing’s ambitious space programme.
The day before, the United Arab Emirates’ “Hope” probe also successfully entered Mars’ orbit, making history as the Arab world’s first interplanetary mission.
Chinese spacecraft nearing Mars, world’s 2nd in 2 days
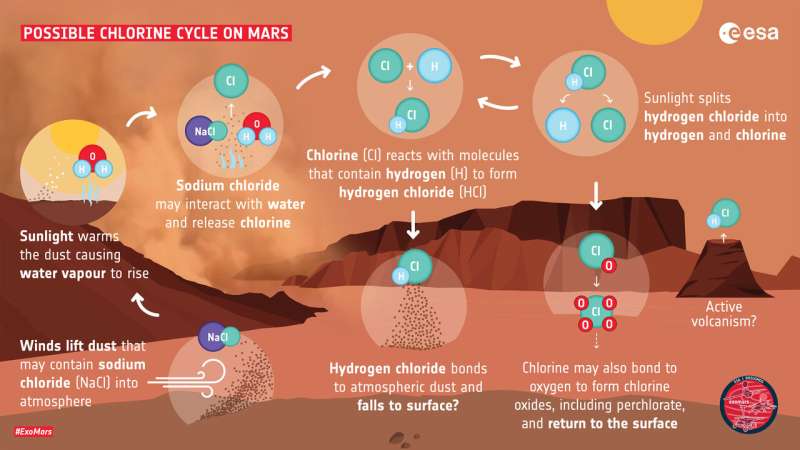
Oleg Korablev et al. Transient HCl in the atmosphere of Mars, Science Advances (2021). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe4386
© 2021 AFP
Citation:
Scientists detect water vapour emanating from Mars (2021, February 10)
retrieved 10 February 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-02-scientists-vapour-emanating-mars.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
If you liked the article, do not forget to share it with your friends. Follow us on Google News too, click on the star and choose us from your favorites.
For forums sites go to Forum.BuradaBiliyorum.Com
If you want to read more Like this articles, you can visit our Science category.



